A significant percentage of multinational companies in the world today started as small businesses. Some started with as little as five employees, a meager income, but incredible resilience.
Interestingly, most start-ups usually begin by selling a single product or offering a single service before enlarging their scale to feature other related goods and services. Recently, the world has seen a high rise in the emergence of start-ups. This event can be attributed to the illumination of entrepreneurship as the key to economic development.
As an investor or entrepreneur, before establishing a new business, there are a few things you might ask.
Such includes questions like What’s the average rate of start-up success in different parts of the world? How do start-ups get the funding needed to grow the business? What’s the impact of the world's economy on start-ups? This article can provide some answers to your questions.
Key Startup Statistics
- Startup entrepreneurs can spend 40% of their working hours on tasks that do not generate income (hiring, HR tasks, and payroll).
- About 90% of startups fail and only 10% succeeding every year.
- 20 technology companies that reach $100 million in revenues founded each year in U.S.
- Highest five-year survival rate for new businesses is at 51.3%.
- 69% of U.S. entrepreneurs started their business at home.
We have gathered and compiled statistics about start-ups through our in-depth research.
Interesting Business Startup Facts
1. The United States has the highest number of start-ups.
(Start-up Ranking)
According to this data provided by Start-up Ranking, the United States is the country with the highest number of start-ups, with about 70,762 start-ups. It is followed at a distance by India, which has 12,556 start-ups. The United Kingdom comes third with just 6,155 start-ups. Other countries include Canada, Indonesia, Germany, and Australia, in fourth, fifth, sixth, and seventh, respectively.
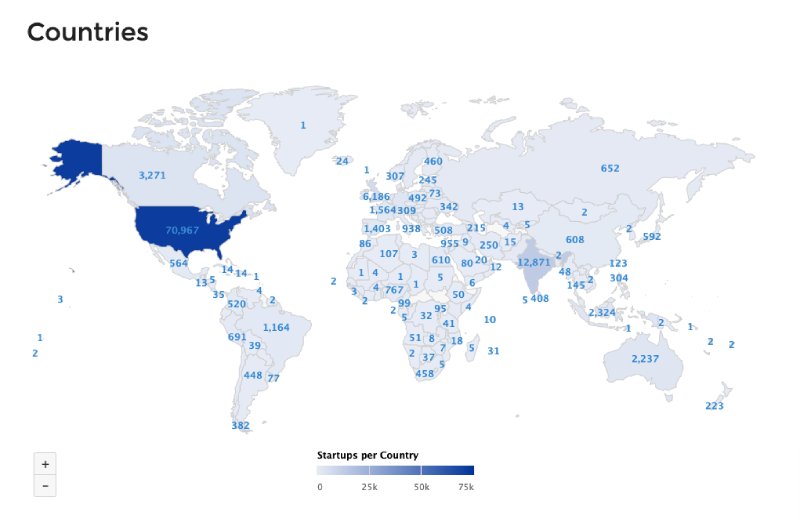
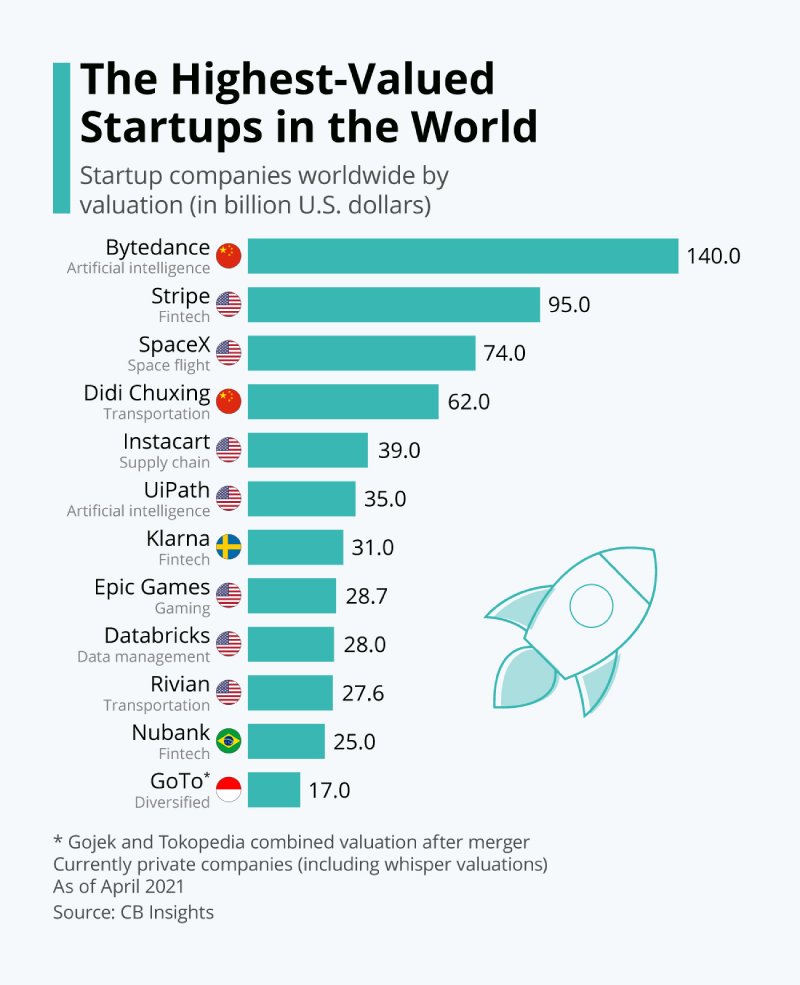
2. Bytedance from China is the highest-priced private start-up today and is worth $75 billion.
(Jewish Review)
In Chine, the most successful start-up today is Bytedance (Toutiao), worth over $75 billion. It is followed by Didi Chuxing, also from China and worth $56 billion. The next on the list is Stripe, a United States Fintech company worth about $36 billion, with Space X coming closely at $33.3 billion. Airbnb, Kuaishou, Paytm are others start-ups following closely on this list.
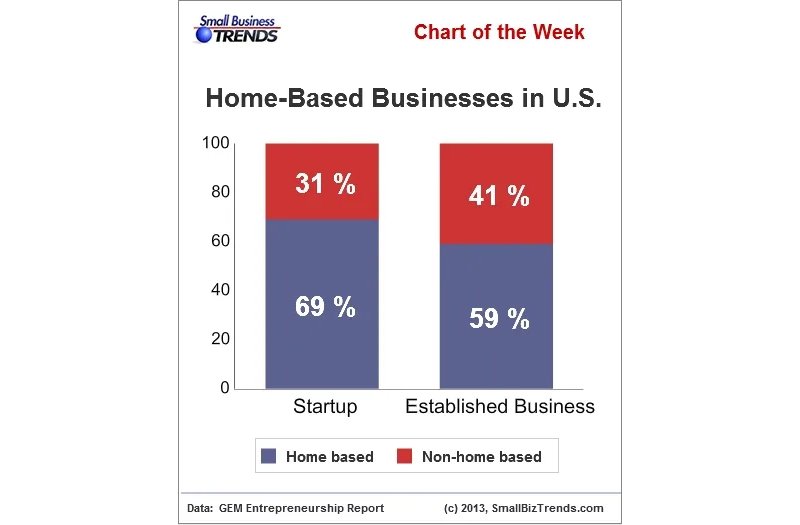
3. 69% of growing start-ups today started from home.
(Small Business Trends)
There is always a starting point for everything, including prominent start-ups today. Most start-ups usually come from their founders' homes. These investors and entrepreneurs try to minimize costs. This is because high costs and low revenues characterize start-ups. Also, it takes a while before major investors start pulling in. What's more surprising is that most start-ups continue their businesses from home even after years of birth.
4. From a recent study, the Fintech industry has the highest number of start-ups.
(Statista)
The Fintech industry has the highest number of start-ups today, with about 7.1%. The life sciences and healthcare industry come next with 6.8%, followed by artificial intelligence and the gaming industries, which have 5.0% and 4.7%, respectively. These statistics point to the fact that most start-ups today are tech-related companies.
Startup Demography Statistics
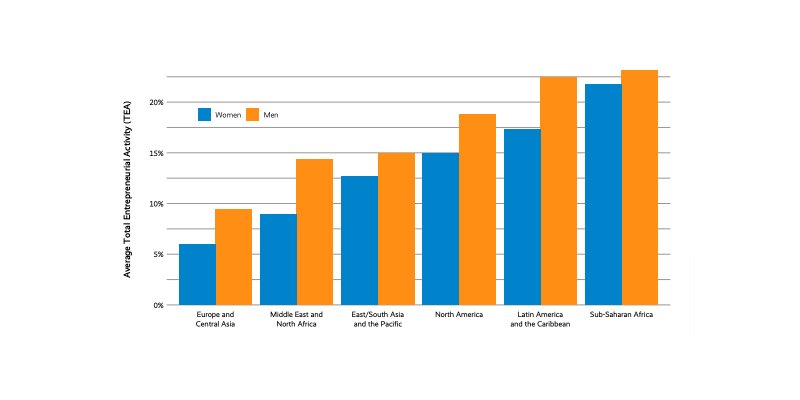
5. As of 2019, there were more male entrepreneurs than females, with a ratio of 10:7
(Global Entrepreneurship Monitor)
There was a time when the margin was much broader than this. A few decades back, finding an organization created and managed by women was rare, especially in developing countries. Although women ran small businesses and offered services tagged ‘for women,' they had less impact in the industry.
However, statistic taken in 2019 by Global Entrepreneurship Monitor shows that the gap between male and female entrepreneurs is closing. This indicates that more women are actively involved in entrepreneurship and start-up creation.
6. In the United States, there are 14.8 million businesses owned by men and 9.9 million businesses by women entrepreneurs.
(Finances Online)
Statistics from Finances Online reveal that men in the United States own about 14.8 million businesses. Women also own a large percentage of companies in the United States, with 9.9 million firms owned by women. This is in total accordance with the previous statistic that reported more men being involved in entrepreneurship than women.
7. A whopping 95% of entrepreneurs in the world today are bachelor degree holders.
(Kauffman Foundation)
This statistic shows that formal education is essential to start or grow any business in today's world. This is because most investors would trust educated people with their money better than the uneducated ones. Also, doing business today requires a level of technicality that uneducated people may not have. Apart from this, the rise in unemployment has pushed many graduates from job seeking to job-creating.
8. Entrepreneurs who had worked at big tech organizations before setting up their businesses performed 160% better.
(First Round Capital)
We're in an age where technology rules almost everything; therefore, having a deeper insight into technology and how to optimize it can help any business grow. Prominent tech organizations try to bridge this gap by training their employees through online courses. If an employee pulls out of the organization afterward, he takes the knowledge acquired with him and can incorporate it into his business as well.
9. Entrepreneurs who attended an ivy league college built start-ups that succeeded 220% more than their counterparts’ start-ups.
(First Round Capital)
This is more proof that the higher the quality of education an entrepreneur has, the more likely the start-up is to succeed.
10. Start-ups owned by female entrepreneurs were 63% more successful than those founded and developed by male entrepreneurs.
(First Round Capital)
Although men found more start-ups, statistics show that women have better skills for growing businesses than their male counterparts. According to First Round Capital, start-ups owned by women were 63% more successful than those founded by men.
Start-up Success And Failure Statistics
11. 80% of successful start-ups founders say even with limited cash flow, they have the needed qualification and ample experience to manage an organization.
(Small Business Trends)
Sometimes, capital is not a limiting factor to having a successful start-up. About 80% of start-up founders have agreed to these stats. This is because a company with all the needed funding still needs the brains and the skills to manage it. Many organizations fail because they put all their effort into sourcing funds and neglect other basics.
12. As of 2017, the United States healthcare industry had the highest number of start-ups pulling in a revenue of about $36.3 billion.
(Inc.)
The number of healthcare start-ups worldwide has skyrocketed, making about $36.3 billion alone in the U.S. This could be attributed to the healthcare industry's union with tech companies.
13. 14% of start-ups said neglecting customers’ needs was the cause of their failure.
(Fundera)
Customer service is paramount to growth, but many start-ups neglect this. Research has shown that many start-ups focus on advertising, developing better products, and improving their business model than their customers. Interestingly, customers service is crucial to the growth of a business. When customers don’t get what they want, they move on to the competition that can provide for their needs.
14. Mining has a 51.3% five-year survival rate which is the highest in all industries to date.
(US Census Bureau)
Many start-ups fail in the first one to two years of business, but it is different for the mining industry. More than half of mining start-ups have an average lifespan of five years.
15. The number of start-ups that generally fail is about 90%, while 10% fall in the first year of starting, and 70% fail between 2 – 5 years.
(Failory)
This statistic shows that only about 30% of start-ups last five years. A whopping 70% cannot hold the business for that long.
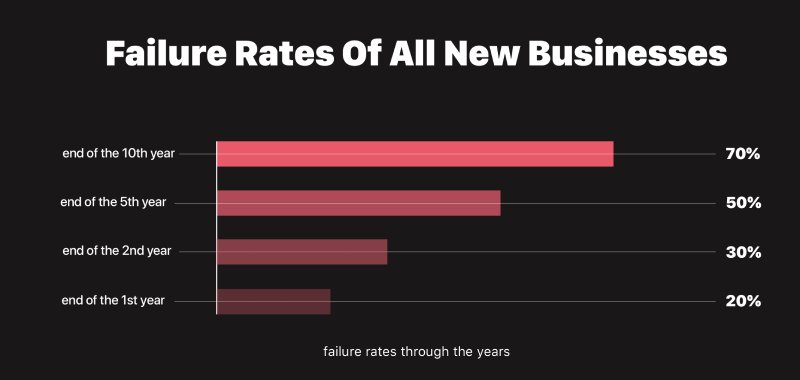
16. Start-ups fail because of high competition in the first 3 – 5 years of activeness.
(Failory)
This statistic could be because as each year passes, the number of start-ups increases. As a result, more competitors enter into the domain with improved business models and strategies that overcrowd the existing ones.
17. 29% of entrepreneurs identify lack of funding as the second most significant reason for the failure of start-ups
(CBInsights)
Start-ups are likely to fail 90% of the time without adequate funding. As a result, most start-ups incur long-term debts in a bid to fund the business.
18. 23% of start-ups fail due to lack of a good business team, while 19% are eventually overshadowed by competition
(CBInsights)
CBIsights and several other sources, through surveys and research, have proven that teams are significant contributors to a start-up’s success or downfall. While 23% fail due to bad teams, 19% are crushed by the competition. This statistic proves that any start-up willing to enter into a competitive domain must be fierce with its marketing, resilient with its work models, and always be creative enough to make a comeback.
19. There is not much variation in the start-up failure rate across all industries
(SBA)
What differentiates start-ups when it comes to successes and failures are the type of business, the business model, the entrepreneur, funding, amongst many others, not the industry under which the company falls.
20. As of 2018, 82% of businesses went under because of financial problems
(Fundera)
Funding remains a significant problem for many businesses today. Even with the birth of numerous funding schemes and an increased number of investors, some factors inhibit certain start-ups from benefiting from the multiple funding schemes. Financial problems range from lack of adequate capital, long-term debts that swallow up the company's revenue, bankruptcy, and more.
21. 80% of small businesses survive in the first year of business
(Fundera)
According to Fundera, 80% of start-ups will perform well in their first year in business, but only about 70% will scale through the second year. Only half of the small businesses will remain in business up to the fifth year, and a tiny fraction of start-ups, about 30%, end up reaching ten years in business.
22. There’s a 30% probability that entrepreneurs who have performed well in other businesses will equally succeed in their next start-up.
(Skill vs. Luck in Entrepreneurship)
Experience is vital in any sector of life, and this is no different for business. People who have ventured into other businesses at some point have probably failed and learned from these failures. Even if it’s just marketing knowledge that was amassed in the previous company, they're better off with it than new founders.
Start-up Trend Statistics
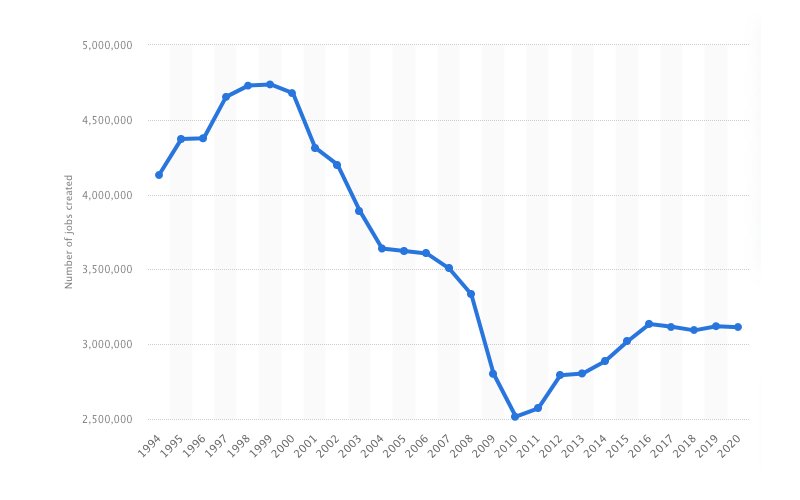
23. The rise of start-ups led to an increase of 2 million jobs in the United States in 2015
(U.S CB)
More start-ups mean more job opportunities. Statistics show that the United States has the highest number of start-ups. However, other countries have also seen a tremendous rise in available jobs. This statistic is proof that there will be more job opportunities in the future as the number of start-ups continues to increase.
24. It takes about 22 months to move from Seed to Series A, 24 months from Series A to Series B, and 27 months to move from Series B to Series C.
(Carta)
The first venture capital financing is usually the hardest to get because the most work is done to convince investors that the start-up is profitable.
25. As of 2018, the United States had 30.2 million start-ups.
(SBA)
This number can be attributed to the fact that the United States has been one of the countries that have encouraged the growth of start-ups, followed by China over the years.
26. In 2010, there was only an average of $5 million Series A, but as of 2017, it had hit $12 million.
(TechCrunch)
With the growth and development experienced in the business world, statistics reveal that start-ups have contributed immensely to the economy. This is evident from the recent rise of valuable start-ups, as investors are no longer hesitating to fund start-ups like they used to. Instead, when investors scout a promising start-up, they go all in for it.
27. In 2017, 67% of series A start-ups said they were already making steady income before receiving funding.
(TechCrunch)
Not surprising since revenue stream is one of the things investors consider before pouring in their money. This is not a plus for start-ups, but that’s just the way things work.
Startup Cost and Funding Statistics
28. The average pay for five employees across the United States is estimated to be $300,500 making payroll one of the highest costs of start-ups.
(Smart Asset)
When a company is going through a crisis, the first thing they do is to downsize employees as cost control. This is because human resources incur one of the most significant expenses of any organization, irrespective of size. This remains a big problem for entrepreneurs.
Also, start-ups need to employ professionals as a part of their team, but, most times, they can’t afford these bills. Based on this, research indicates that if the cost of the workforce is removed, 80% of failed businesses will survive.
29. Most start-ups would need about $10,000 to $125,000 worth of equipment to set up.
(Fundera)
Setting up a business is not free, especially if you’re a production company. Research reveals that start-ups in the manufacturing and healthcare industries require the most capital to set up. There’s the cost of office space, facilities, employees’ pay, insurance, publicity, and more. Therefore, most start-ups will need about $10,000 to $125,000 worth of equipment to set up.
30. As of 2018,77% of start-ups were financed by the founders.
(Lendio 2018 Survey)
Today, most start-ups are fuelled by their founders. This is because it is challenging to have investors invest in a business yet to yield sufficient income. However, with the rise of several funding options for start-ups, the number of start-ups financed by the founders is reducing.
31. The average entrepreneur earns only about $59,000
(Finances Online)
Heavy expenses and small revenue characterize start-ups. Most start-ups take numerous losses in the first few years of the business. However, this is just an average as some may earn more or less. This shows that the income of an entrepreneur is a function of different things.
32. According to recent research, accounting, online retail, and landscaping start-ups spent under $5,000 to set up.
(Small Business Trends)
We can attribute this low cost to the fact that start-ups in this category offer services rather than produce goods, and their services do not require a lot of human resources or machinery.
33. Medical offices, restaurants, and manufacturing companies are the most costly to set up, needing an average capital of about $100,000
(Small Business Trends)
This statistic is not surprising because these companies usually require standard facilities and equipment for quality service. Hospitals and restaurants need to maintain a healthy space every second, and manufacturing companies spend a lot on maintenance.
34. Most of the prominent start-ups today have taken a billion-dollar loan on average as funding at some point.
(PitchBook)
Risk-taking is a significant part of growing any business. Some of these risks include loans. Statistics show that most prominent start-ups have taken up to a billion dollars worth of loans at some point. Sadly, sometimes risks put businesses in years of debt. Therefore, it is advisable to create a proper risk assessment and management plan before taking a first-time business loan like these prominent start-ups.
35. The cost of health insurance is one of the dominant challenges start-ups faces
(NSBA)
Many organizations in today’s world, especially those whose jobs pose a risk to the employees' health, are mandated to provide health insurance. Due to the cost of health insurance, many start-ups cannot hire as many employees as they need to, which reduces the productivity of the start-up.
36. According to a survey carried out by NSBA, approximately one in four start-ups became limited because they could not receive funding.
(Fundera)
Funding is essential, especially for start-ups with newer business models. For example, suppose a start-up is into a novel type of business. In that case, investors will usually consider the amount of time it will take the market to accept the service or product the start-up is offering. Unfortunately, that's usually where the problem lies because most start-ups of this kind require enormous funding due to their novelty.
37. In 2018, male entrepreneurs received $109.36 billion in VC while female counterparts only received about $2.86 billion in VC.
(PitchBook)
Male entrepreneurs have always been in the market for as long as forever. Still, women are just starting to get recognition as a part of the business world, especially in many developing countries, thanks to the gender movement for years now. Of course, this statistic shows the wide margin between the two genders, but without a doubt, the margin will become closer in years to come.
Startup Team Statistics
38. It takes an average of 6 months for start-ups to get employees.
(Forbes)
Many people do not apply to work for start-ups for tangible reasons. This is because most start-ups are not stable. They could shut down at any time, and the workers would be displaced. Another reason is start-ups do not pay much. The majority of start-ups want to hire the best but cannot afford their payroll. This turns a lot of people off. On the other hand, employment at well-established companies comes with many perks. This includes life insurance, training, vacations, and more, some or all of which start-ups may not be able to afford.
39. Partnership start-ups beat sole proprietor start-ups in performance by 163%.
(First Round Capital)
When two entrepreneurs or businesses collaborate to birth a single company, they stand a higher chance of surviving. A primary reason why start-ups fail is most start-ups are sole proprietorships. Therefore, the burden of financing, managing, organizing, decision-making, and strategizing falls on one person.
40. 23% of start-ups said team-related problems constitute a significant contribution to their failure.
(Entrepreneur)
With the wrong teamwork, even well-established companies could fail. Teamwork is an essential part of any start-up, especially the founding team, as most of the decision-making and strategizing are done by this team. Team-related problems could be the incapability of the team leader, bad relationships among team members, and even lack of the right people on the team. Any start-up willing to grow must be ready to create efficient teams.
Technology Start-up Statistics
41. The United States tech market was worth a whopping $1.6 trillion as of 2019.
(CompTIA)
The United States has been the home for tech start-ups over the years. The world's biggest tech companies are based in the US, contributing to the enormous value in the tech market. CompTIA statistics show that the United States tech market was worth a whopping $1.6 trillion as of 2019.
42. In 2018, the tech industry recorded a 63% start-up failure rate.
(Failory)
This is the highest failure rate across the industries so far. Tech start-up failure can be credited to many reasons, one of them being the fierce competition in the industry. Already existing tech brands are constantly improving to always stay at the top.
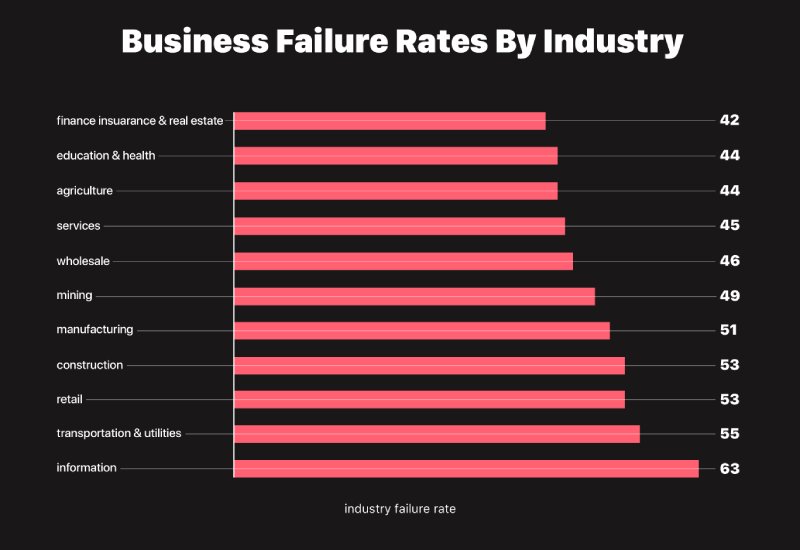
43. From 2007 to 2016, electronics manufacturing went up by 78%.
(ITIF)
As technology advances, more discoveries are made. Over the years, technology has contributed to the world's economy, with a significant rise in tech products in most companies. An example is the Artificial Intelligence sector. Robots were strange and luxurious many years back, but today, several household and office robots are flooding the market.
44. Tech companies pay $102,000 more than the average pay of workers in the United States, which is $48,000.
(Forbes)
Undoubtedly, the tech market is enormous, with lots of opportunities. This provides many tech start-ups with a high chance of success. Statistics show that many tech start-ups are likely to be worth billionaires in just a few years.
45. In the United States, an average of 20 tech companies are created every year.
(Kauffman)
As mentioned earlier, the United States is home to many tech companies. However, regardless of the fierce competition, more entrepreneurs continue to troop into the tech sector every year.
Conclusion
Experts believe that any start-up can succeed if the entrepreneurs follow success principles keenly. However, entrepreneurs still have to add a little bit of fluidity to make room for creative thinking. This is a vital backbone of entrepreneurship.
Another thing to not lose sight of is value. If the product or services a start-up offer loses its value, the start-up will most likely run out of business. Also, as a start-up founder or an entrepreneur, always focus on the stats because the numbers keep fluctuating from time to time. What worked yesterday may not work today or in the future.
References:
- StartupRanking
- Esei Business School
- Jewish Review
- Serious Startups
- SmallBizTrends
- Failory
- Accounts and Legal
- Quickbooks
- Hexgn
- Toptal
Ludjon, who co-founded Codeless, possesses a deep passion for technology and the web. With over a decade of experience in constructing websites and developing widely-used WordPress themes, Ludjon has established himself as an accomplished expert in the field.






Comments